Qualcomm launched Snapdragon 765G on December 5, 2019, a premium 5G-ready mid-range processor. Regarding specifications, Snapdragon 765G is similar to Samsung’s Exynos 980, launched on September 4, 2019. MediaTek has also unveiled its mid-range 5G SoC, Dimensity 1000L MT6885. For consumers waiting for mid-range 5G smartphones, these three processors will end their wait in 2020. So, we will discuss the comparison between Snapdragon 765G, Exynos 980, and Dimensity 1000L MT6885 based on their key specifications.
Snapdragon 765G Vs Exynos 980 Vs MediaTek Dimensity 1000L
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
All three 5G processors come quite close to each other regarding performance/specification. All of them are octa-core SOCs.
If we look at Snapdragon 765G cores, it consists of one ARM Cortex-A76 based Kryo 475 Prime core at 2.4 GHz, one ARM Cortex-A76 based Kryo 475 Gold core at 2.2 GHz, and six ARM Cortex-A55 based Kryo 475 Silver cores at 1.8 GHz. The first core, clocked at 2.4 GHz, is dedicated for high demand tasks, then the second core, clocked at 2.2 GHz, is dedicated to somewhat moderate performance demanding tasks, and the rest of the six cores clocked at 1.8 GHz is power-efficient cores for normal day to day tasks.
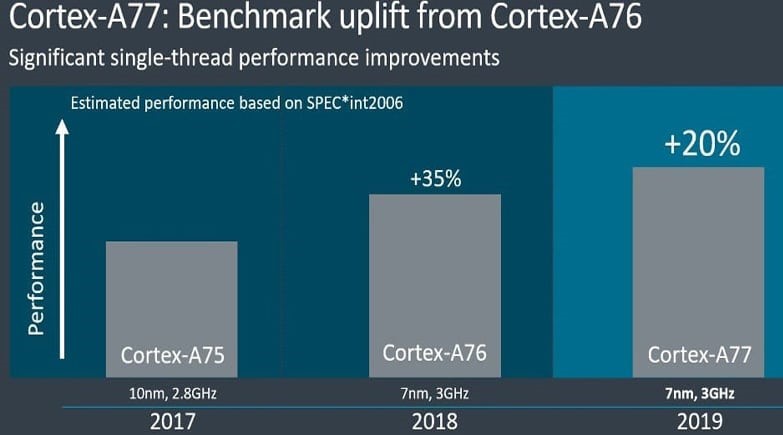
Then, coming to the Exynos 980, it consists of two Cortex-A77 cores at 2.2 GHz and Cortex-A55 cores at 1.8 GHz. The first core, clocked at 2.2 GHz, is dedicated to high-demand tasks like gaming and other stuff where higher frequency cores are required, and the rest of the six cores clocked at 1.8 GHz are power-efficient cores for normal day-to-day tasks.
On the other hand, MediaTek’s Dimensity 1000L chipset has four Cortex-A77 cores with a clock speed of 2.2GHz for high performance. The remaining four cores come with Cortex-A55 at 2.0GHz for power efficiency and mid-performance.
So, after looking at the detailed specifications of CPU cores, we can say All three of them are quite similar to each other.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
According to Qualcomm’s claim, Snapdragon 765 G’s GPU Adreno 620 got a 38% performance boost compared to the last-gen Adreno 618 GPU. So performance-wise, it’s quite a nice upgrade from last-gen. In contrast, Samsung’s Exynos 980 uses its last-gen flagship SOCs GPU this time. A Mali-G76 in an MP5 configuration is used in Exynos 980, but they cut the core count to less than half compared to last-gen flagship GPU. For Dimensity 1000L, we have ARM’s Mali-G77 GPU, which is the highest-performing mobile GPU for complex use cases.
We have to wait until some GPU benchmarks hit the market to see how each GPU performs. However, on paper, 1000L has dominated the GPU section as it uses the Mali-G77 series.
Manufacturing Process
Here in the manufacturing process, Snapdragon 765G takes this round. Snapdragon 765G is built using Samsung’s 7nm EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) process. In contrast, Samsung’s Exynos 980 is made using Samsung’s 8nm FinFET LPP (Low Power Plus) process. On the other hand, MediaTek’s Dimensity 1000L is fabricated on TSMC 7nm process. So we can say the Snapdragon 765G with EUV version is more power-efficient compared to the Dimensity 1000L (2nd Position) and Exynos 980 (3rd Position).
Memory
All of them use the LPDDR4X memory type. So, in terms of memory performance, all SOCs are equal. Snapdragon 765 G’s memory is clocked at 2133 MHz, but Samsung’s Exynos 980 and MediaTek’s Dimensity 1000L have not disclosed this number.
AI Performance
In AI performance, Snapdragon 765G can perform over 5.4 trillion operations per second (TOPS). For AI performance, 765G uses its Hexagon 696 DSP and HVX with Tensor. By using its CPU, GPU, HVX, and Tensor, it outputs 5.4 TOPS of raw AI computing power.
The Dimensity 1000L integrates MediaTek’s AI Processing Unit 3.0, capable of performing 4.5 TOPS. That means 765 G’s AI Engine is more powerful than 1000L’s AI Engine.
Coming to the Exynos 980, Samsung hasn’t shared any details except it is using Samsung’s in-house NPU engine, which is integrated into the SOC. So, it’s very hard to decide its performance in the field of dedicated AI tasks.
Display
If we talk about display, Snapdragon 765G can support QHD+ (3200 x 1800) at a 60 Hz refresh rate and FHD+ at 120Hz. In contrast, Exynos 980 can support WQHD+ (3360 x 1440) at a 60 Hz refresh rate, and Dimensity 1000L can support FullHD+ at 120 Hz and 2K+ at a 90 Hz refresh rate.
As all of them are midrange SOCs, we can’t expect high refresh rate support in high resolution. So, in terms of display, all of the processors are almost equal.
Camera
For the camera Snapdragon, 765G uses Qualcomm’s Dual 14-bit Spectra 355 ISP. This Spectra 365 ISP can process images up to 192MP in size, 36MP images with ZSL (Zero Shutter Lag), or 22MP images with ZSL in dual camera mode. For slow-mo videos, it can record 480fps videos at 720p. Also, it supports HDR10+ in video recording. It supports HDR10, HDR10+, HLG, and HEVC video formats. Snapdragon 765G can capture 4K HDR video in portrait mode, and it uses 10-bit color depth video capture.
In contrast, Exynos 980 can capture 108MP images in a single camera and 20MP images in dual camera mode. Also, it supports 10-bit 4K UHD 120fps encoding and decoding with HEVC (H.265), H.264, and VP9 formats.
The Dimensity 1000L with 5-core ISP can support up to 80MP single camera and 32MP+16MP dual camera. This ISP also provides support for 4K HDR video capture, but the company has not confirmed whether it is cable of HDR10+ encoding and decoding.
So we can say Snapdragon 765G is slightly ahead in the camera department compared to Exynos 980 and Dimensity 1000L.
Connectivity
All three chipsets use integrated modems for connectivity.
Snapdragon 765G uses Qualcomm’s X52 Integrated Modem-RF system. For the 5G Spectrum, it supports Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), mmWave, and sub-6 GHz spectrums. Qualcomm claims 3.7Gbps DL (download link) and 1.6Gbps UL (upload link) for 5G, whereas 1.2Gbps DL and 0.21Gbps UL for LTE network connectivity.
In contrast, Exynos 980 uses a Shanon Integrated modem. Samsung claims 2.55Gbps DL and 1.28Gbps UL for 5G, whereas 1Gbps DL and 0.2Gbps UL for LTE network connectivity.
The MediaTek Dimensity 1000L’s integrated 5G NR (Sub-6GHz) modem can provide a download speed of 4.7Gbps and an upload speed of 2.3Gbps.
Which One is Better Chipset?
If we compare them according to their specifications, we don’t see a clear winner here. All of these SOCs are almost equal in terms of specifications. But Antutu benchmarks show a different story.
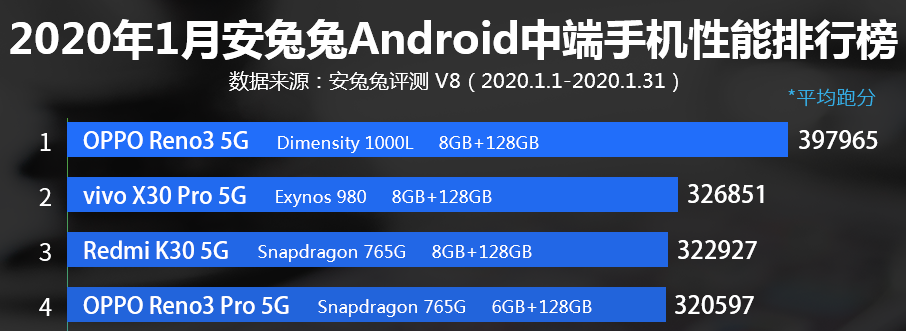
Antutu has also officially published benchmark scores of the most powerful mid-range 5G phones. Dimensity 1000L powered Oppo Reno 3 pulled an average score of 3,97,965 points. On the other hand, Exynos 980-powered Vivo X30 Pro 5G and Snapdragon 765G-powered Redmi K30 5G came off with an average score of 3,26,851 points and 3,22,927 points, respectively.
So, we can clearly see MediaTek Dimensity 1000L is a better SOC in terms of performance if we compare the three of them head to head.




Kan
dimensity 100L is kind of a flagship chips while the other 2 are upper-midrange..